Module 13: Configuring and Managing DHCP & WINS in Microsoft Windows Server 2016/2019
New DHCP Functionality in Microsoft Windows Server (2016/2019/2022)
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) in modern Windows Server versions brings enhanced performance, security, and high availability. Below are key improvements and new functionalities introduced:
New Features and Enhancements
1. DHCP Failover
Purpose: Provides high availability of IP addressing by replicating lease information between two DHCP servers.
Modes:
Hot Standby: One server is active, the other is on standby.
Load Balance: Both servers respond to DHCP requests.
2. DHCP Policy-Based Assignment
Enables custom DHCP options based on conditions:
MAC address
Vendor Class
User Class
Client Identifier
Example: Assign static DNS or gateway to IP phones only.
3. DHCP Server Role in Windows Server Core
DHCP Server role is fully supported in Server Core, improving security and reducing resource overhead.
4. PowerShell Support
Complete management using PowerShell:
Get-DhcpServerv4Scope
Add-DhcpServerv4Reservation
Improved Logging and Auditing
Enhanced logs help track DHCP lease assignments, conflicts, and rogue detection.
6. DNS Dynamic Updates Integration
Improved secure dynamic updates between DHCP and DNS for Active Directory domains.
7. IP Address Conflict Detection
Before issuing a lease, DHCP can perform ping tests to avoid assigning used IPs.
- Unauthorized DHCP Server Detection
- Integration of DHCP with DNS
- Expanded Scope Support
- Support for Option Classes
- Automatic Assignment of IP Addresses
- Enhanced Monitoring and Statistical Reporting
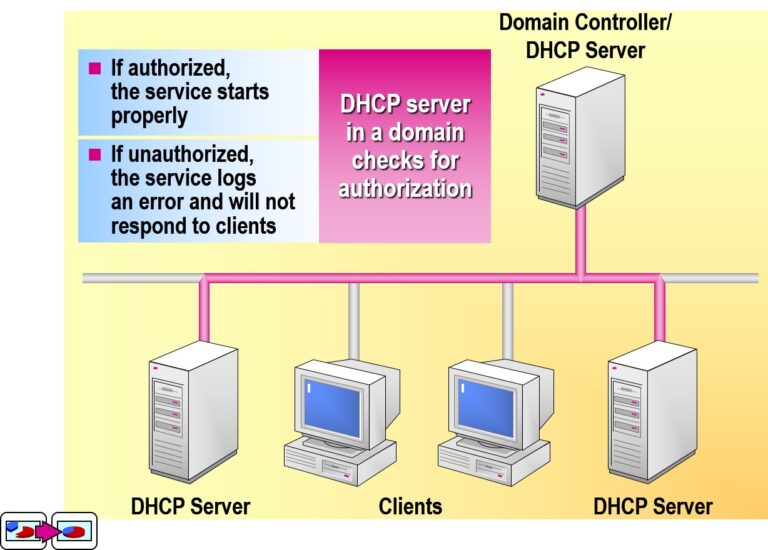
Authorizing a DHCP Server in Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS)
To prevent unauthorized DHCP servers from handing out IP addresses in a network, only authorized DHCP servers are allowed to operate in Active Directory environments. Here’s a quick guide:
What Is DHCP Server Authorization?
Authorization is a security feature that ensures only DHCP servers registered in Active Directory can issue IP addresses in a domain-joined network.
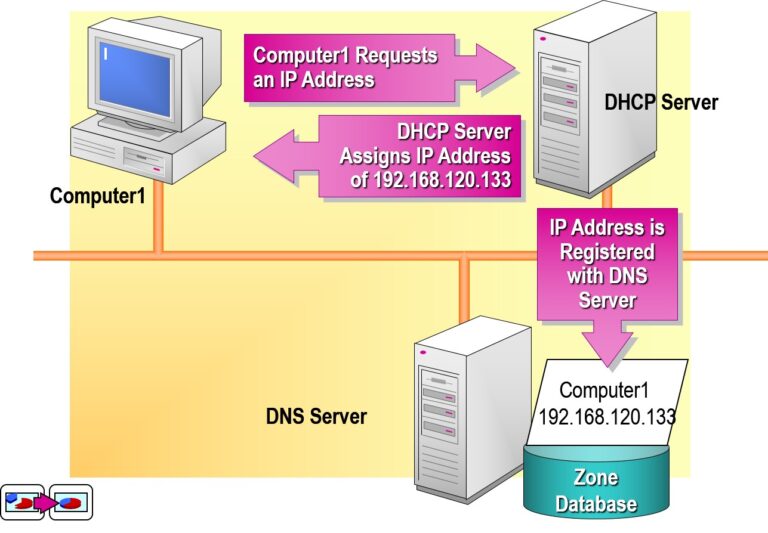
Examining Dynamic Update of DNS Servers in Windows Server
Dynamic Update allows DNS client computers to automatically register and update their resource records (such as A and PTR records) with a DNS server.
What Is Dynamic DNS (DDNS)?
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) enables automatic registration of hostnames and IP addresses into the DNS database without manual intervention.
Configuring a Scope in DHCP (Windows Server)
A DHCP Scope defines a range of IP addresses and associated configuration parameters (like gateway, DNS) that a DHCP server can lease to clients on a subnet.
What Is a Scope?
A scope is a pool of IP addresses and settings (called DHCP options) used to dynamically assign network configuration to clients.
- Configuring a Scope
- Name
- IP Address Range
- Subnet Mask
- IP Address Exclusions
- Lease Duration
- Common DHCP Options
- Gateways
- Domain name and DNS servers
- WINS servers
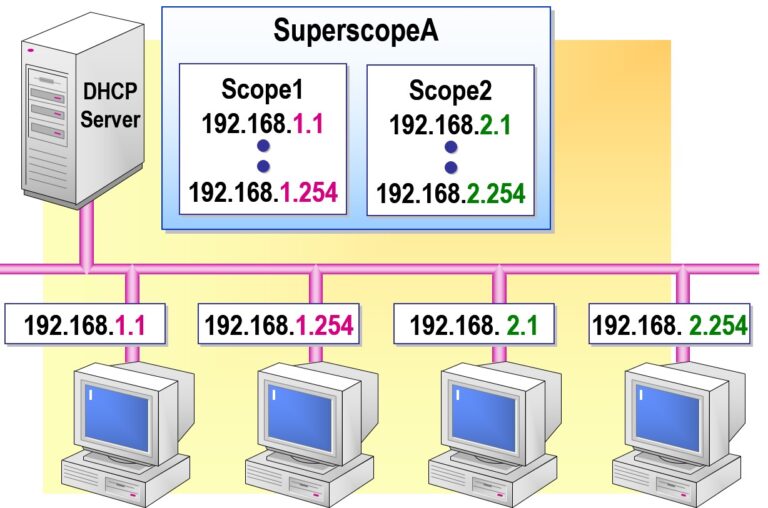
- Configuring a Superscope
Step-by-Step: How to Configure a Scope
Open DHCP Manager
Start →
dhcpmgmt.msc
Expand Your Server Name → IPv4
Right-click IPv4 → New Scope
New Scope Wizard
Name the scope (e.g.,
Office LAN)Add a description (optional)
Define IP Address Range
Example:
Start:192.168.1.100
End:192.168.1.200
Enter Subnet Mask
Typically:
255.255.255.0
Add Exclusion Range (Optional)
To prevent certain IPs from being assigned.
Set Lease Duration
Default is 8 days; adjust as needed.
Configure DHCP Options
Router (Default Gateway):
192.168.1.1DNS Server(s): e.g.,
8.8.8.8Domain Name:
yourdomain.local(optional)
Activate Scope
Choose “Yes, I want to activate this scope now.”
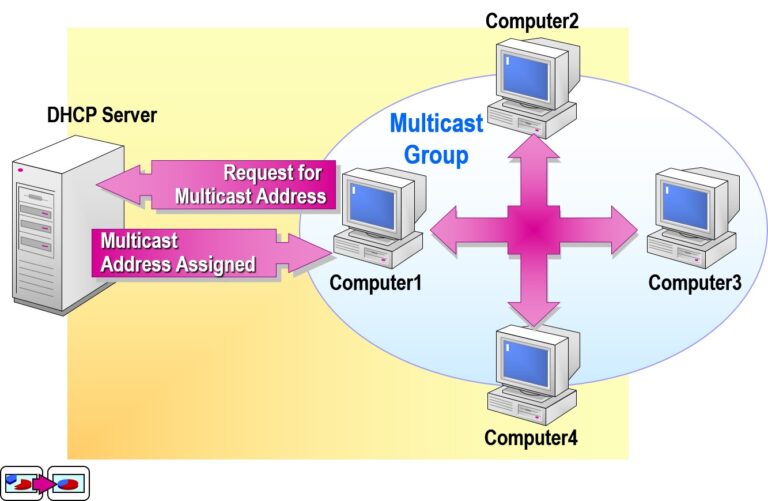
- Configuring a Multicast Scope
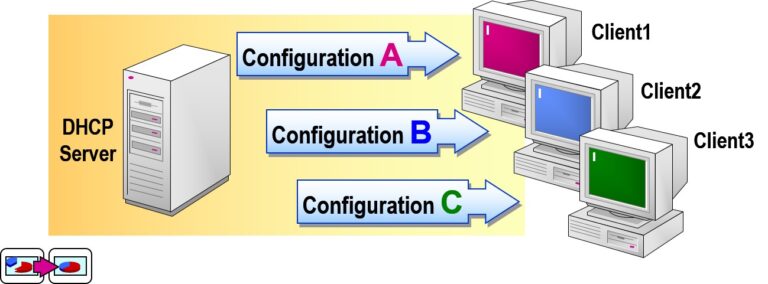
Examining Option Classes in DHCP (Windows Server)
Option Classes in DHCP allow administrators to assign different sets of DHCP options to different types of clients or devices. This makes DHCP highly flexible in complex networks.
What Are DHCP Option Classes?
Option Classes are predefined or custom categories that help deliver specific DHCP options based on:
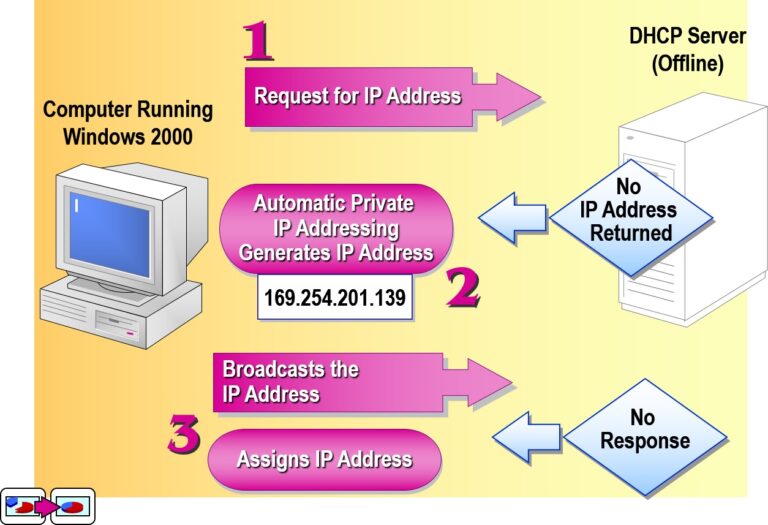
Examining Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA)
Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) is a feature in Windows operating systems that automatically assigns an IP address to a device when the DHCP server is unavailable and no static IP is configured.
What is APIPA?
When a DHCP client fails to contact a DHCP server, Windows assigns a private IP address from the 169.254.0.1 to 169.254.255.254 range, with a subnet mask of 255.255.0.0.
Key Points:
IP Range:
169.254.x.xSubnet Mask:
255.255.0.0No Default Gateway assigned
Used for local communication only (e.g., small peer-to-peer networks)
Not routable on the internet or larger networks
New WINS Functionality in Microsoft Windows Server
WINS (Windows Internet Name Service) is a legacy name resolution service that maps NetBIOS names to IP addresses, primarily used in older Windows networks. While WINS has been largely replaced by DNS, newer versions of Windows Server added stability, manageability, and integration features for environments that still rely on WINS.
What’s New or Improved in WINS (Windows Server 2016/2019/2022):
1. ✅ Better Integration with Active Directory
Though WINS is not directly part of Active Directory, its integration is smoother with updated MMC consoles and Group Policy support for centralized configuration.
2. 📈 Improved Database Stability
Enhancements in the Jet Database Engine used by WINS reduced corruption and improved database repair and cleanup functions.
3. 🛡️ Enhanced Security
WINS now operates more securely under the Windows service architecture, benefiting from Windows Server security hardening, such as:
Better event logging
Support for Access Control Lists (ACLs) on WINS objects
4. 📊 Improved Replication Efficiency
Optimized replication between WINS servers minimizes traffic and allows faster convergence across sites.
WINS replication supports push/pull methods with better filtering and conflict resolution.
5. 🧰 Administrative Tool Enhancements
The WINS management console now includes:
Better filtering/search options
Updated logging interface
More reliable manual database entry management

- WINS Server Functionality
- Persistent Connections
- Manual Tombstoning
- Improved Management Capabilities
- Filtering and searching for records
- Deleting both dynamic and static records
- Selecting multiple records
- Checking database consistency
- Exporting WINS data as a comma-delimited text file
- WINS Client Functionality
- Increased Fault Tolerance
- Dynamic Reregistration

Add comment