Module 8: Manage Desktop Environments Using Group Policy in Windows Server 2016/2019
Introduction to Group Policy in Microsoft Windows Server
Group Policy (GP) is a powerful feature of Microsoft Windows that allows administrators to centrally manage and configure operating systems, applications, and user settings within an Active Directory (AD) environment. It is a critical tool for IT administrators to enforce organizational policies, enhance security, and standardize user and system configurations.
- Group Policy Settings
- IntelliMirror Technology
- Establish Enforceable Configurations
- Specify Settings for:
Administrative Templates
Security
Software Installation
Scripts
Folder Redirection
Registry-based policy settings
Options for local, domain, and network security
Central management of software installation
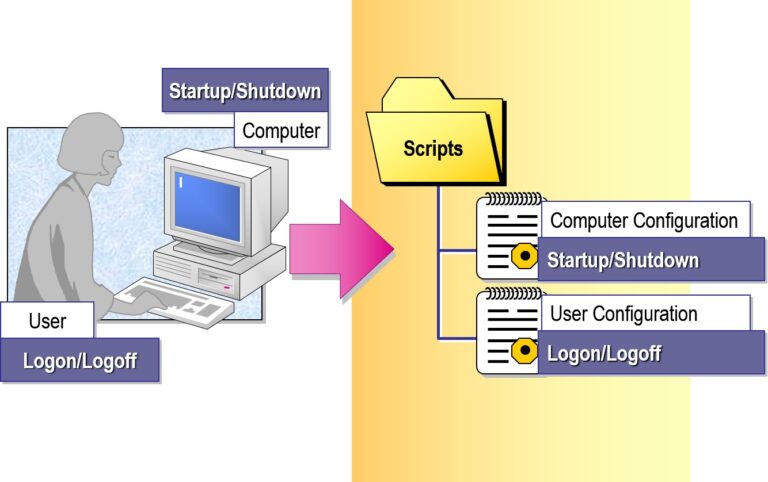
Startup, shutdown, logon, and logoff scripts
Store users’ folders on the network
- Group Policy Objects
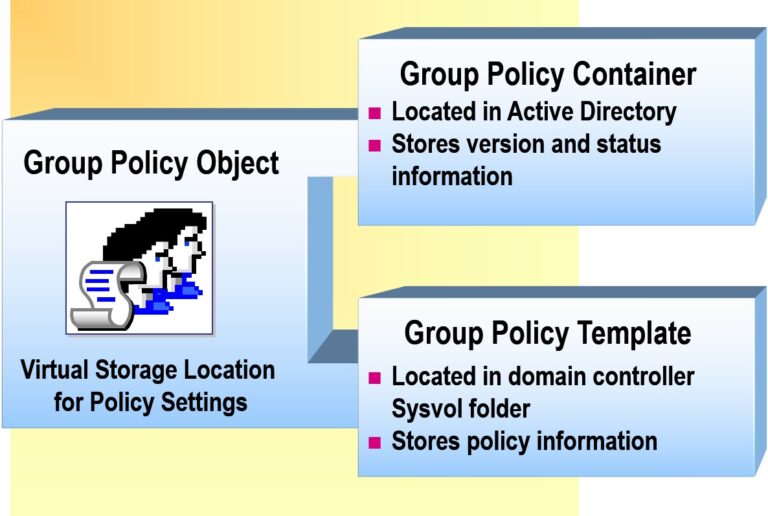
Applying Group Policy
- Inheritance of Group Policy in Active Directory
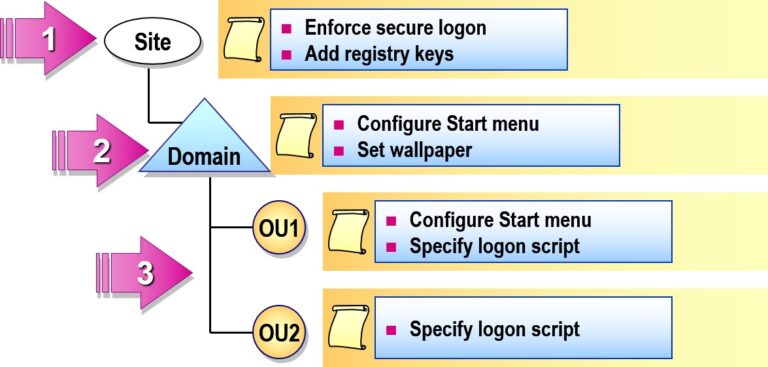
- All domains in the site receive the same security settings
- Accounting receives their own Start menu and the Domain wallpaper
- OU1 and OU2 receive unique logon scripts
- Resolving Conflicts and Modifying Inheritance
- Resolving Conflicts
- Child Not Configured = Parent Settings Apply
- Child Configured, Compatible = Both Settings Apply
- Child Configured, Not Compatible = Child Settings Apply
- Modifying Inheritance
- No Override
- Block Inheritance
- Processing Group Policy Objects
- Windows 10 and 11:
- Applies Computer Settings from Group Policy
- Startup Scripts Run
- Applies User Settings from Group Policy
- Logon Scripts Run
- Group Policy Refreshes on Client Computers Every 90 Minutes and on Domain Controllers Every 5 Minutes
- Creating a Group Policy Object
- Modifying Permissions
- Filtering the Scope of a GPO
- Delegating Control with Permissions
- Changing Processing Order
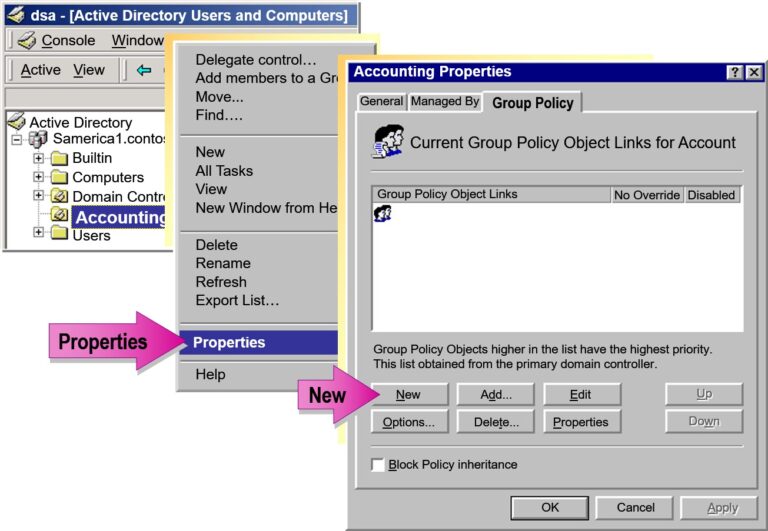
- Managing Group Policy Object Permissions
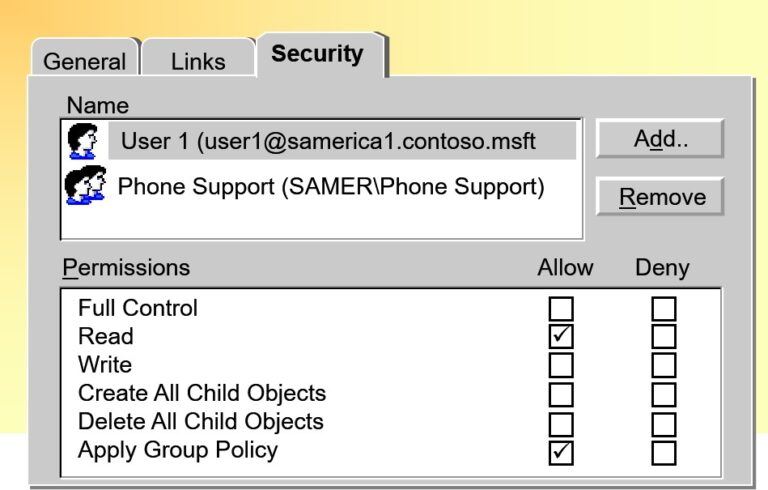
- Managing Group Policy Processing
- Changing Processing Order
- User settings
- Computer settings
- Entire GPO
- Disabling Group Policy Objects
- Deleting Group Policy Objects
Examining the Group Policy Interface
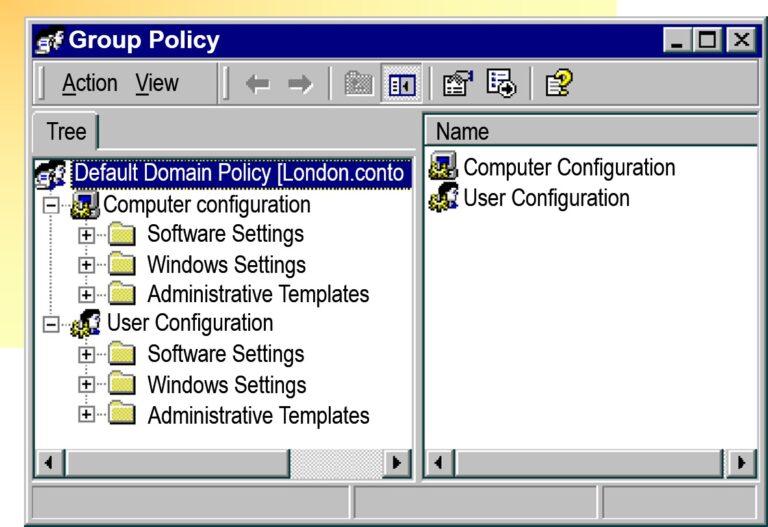
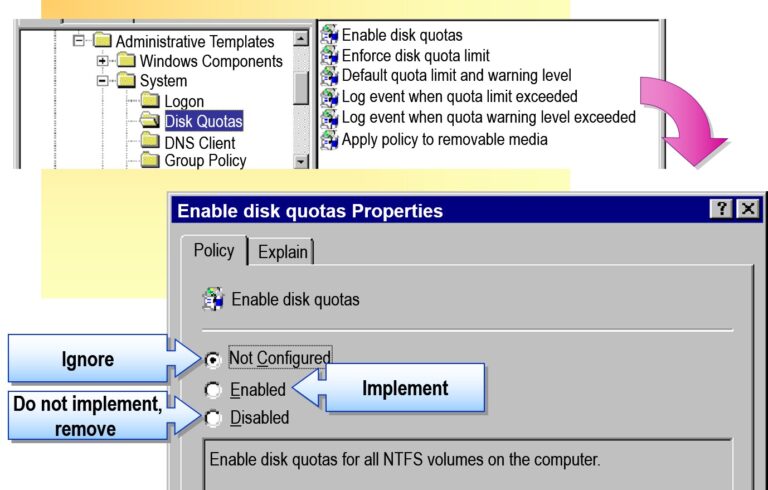
Configuring the Registry by Using Group Policy
Assigning Scripts by Using Group Policy
Redirecting Folders by Using Group Policy
- Examining Folder Redirection Capabilities
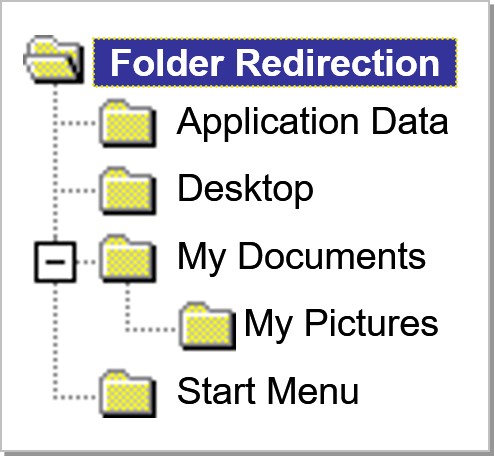
- Create a standard Desktop
- Reduce size of roaming profiles
- Store user data on the network
- Setting a Target Location
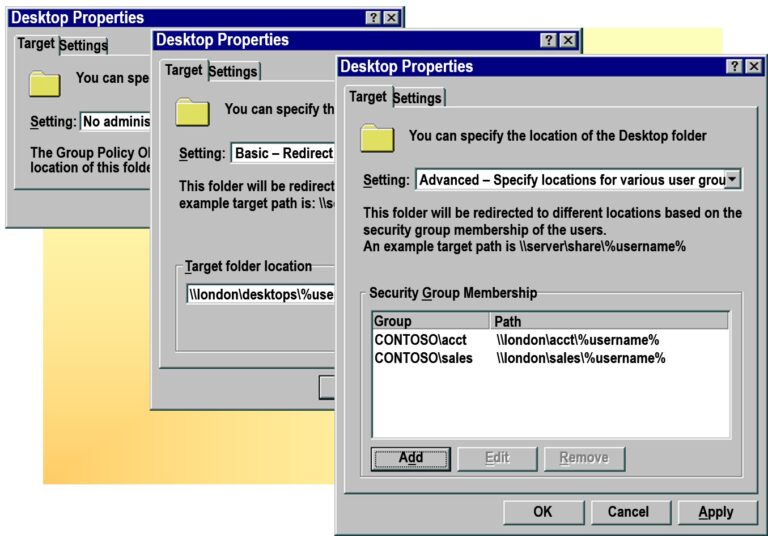
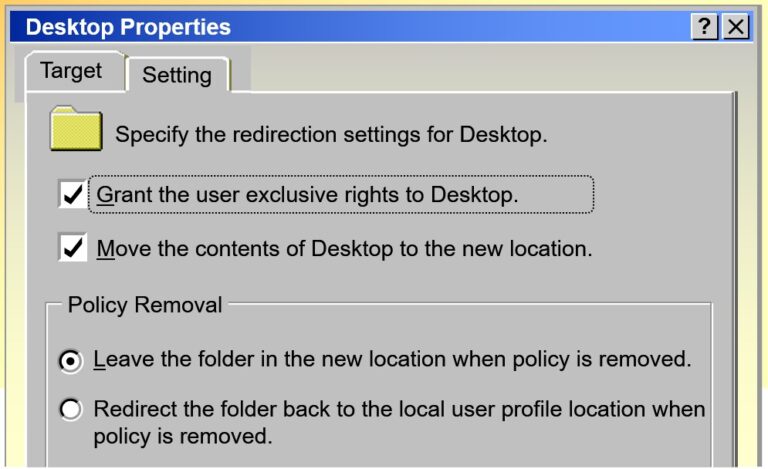
- Configuring Folder Redirection Settings
Guidelines for Implementing Group Policy
- Limit Use of
- Block Inheritance
- No Override
- GPOs linked across domains
- Limit Number of GPOs
- Disable Unused Portion of a GPO
- Group Related Settings in a Single GPO
- Consider Performance and Delegation

Add comment